

圆弧形电解池相比于完全敞开的容器有许多优点。首先监测窗口由圆弧形石英窗口组成,在准直后使光垂直于石英壁入射和出射,减小了光在传播途中的损耗;其次是监测窗口溶液是相对封闭的,减小了测试过程中由于溶液暴露在空气中带来的影响;zui终实现了三电极的放置及Pb薄膜的沉积。
展示全部 
椭偏仪在位表征电化学沉积的系统搭建(十八)- Pb薄膜沉积实验
3.2.6.3 Pb薄膜沉积实验
通过前面实验与分析知溶液及溶液浓度对椭偏仪基底测试影响可忽略,故用该电解池进行了Pb的沉积实验。采用三电极体系(工作电极:Au/Si;对电极:Pt丝;参比电极:Ag/AgCl)。溶液为1M的醋酸钠及1M的醋酸钠与5mM或10mM的醋酸铅。为探究沉积条件,需对工作电极进行CV扫描,扫描速率为5mV/s,扫描电势窗口为-1.2V—0.5V,从开路电压(OCP)开始负向扫描。通过恒压电沉积得到Pb薄膜同时进行400nm到800nm波段的椭偏监测。实验中电极的放置如图3-10所示,Au/Si电极为工作电极置于观察窗口;Pt丝对电极置于工作电极上方(不阻挡光路);将置于鲁金毛细管中的Ag/AgCl参比电极zui大限度接近Au/Si表面。将该在位监测沉积电解池置于椭偏仪的监测台,调节好准直后开始沉积和椭偏监测。

图3-10CV扫描及在位监测Pb沉积实物图
图3-11是对Au/Si基底在醋酸钠和醋酸铅中进行的CV扫描对比图。其中Arccell曲线为1M醋酸钠和10mM醋酸铅中的CV扫描曲线;blank control曲线为1M醋酸钠中的CV扫描曲线;H cell曲线为前期在标准H型电解池中加1M醋酸钠和10mM醋酸铅中的CV扫描曲线。对比Arc cell和H cell两条曲线可以看到,所得到的CV曲线正常,装置可用。该体系下Pb的沉积峰位和溶出峰位大致相同,电流密度与H型电解池所测得的数据相比减小,且在-0.28V左右附近的吸附峰消失。电流密度减小的原因可能有两点,一是电极的有效面积比实际面积小;二是工作电极和对电极不对称。对比Arc cell和blank control两条曲线可知,在只有1M醋酸钠的电解液中电流密度相对于有醋酸铅的可忽略不计。
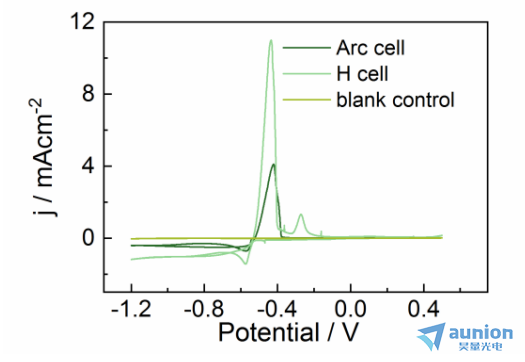
图3-11不同电解池扫描速度5mV/s的CV图
根据CV扫描结果,对Pb薄膜沉积的电压进行选取,为了使得沉积时间更长,使得更有利于椭偏仪测试,所以选了沉积峰位附近的电压,及-0.57V进行Pb薄膜沉积。
图3-12是进行电压沉积过程的电流-时间图,在不同电解液条件下,沉积电压都是-0.57V。其中蓝色表示1M醋酸钠溶液,橙色是以1M醋酸钠加5mM醋酸铅溶液,红色是1M醋酸钠加10mM醋酸铅溶液。从图中可以看到没有醋酸铅存在时电流基本为零,而10mM醋酸铅的沉积电流比5mM醋酸铅的沉积电流大。理论上沉积电流越大,沉积速度也快,相同时间沉薄膜的厚度越厚。所以由电流时间图知只有醋酸钠存在时没有沉积,加入5mM醋酸铅时有沉积但是沉积量比10mM醋酸铅要小。

图3-12沉积电流时间图
图3-13是沉积结果实物图,a图是在1M醋酸钠为电解液沉积后得到的图,可以看到没有沉积物;b图是在1M醋酸钠加5mM醋酸铅为电解液溶液的沉积样品,有灰黑色的明显沉积物,沉积不均匀;c图是在1M醋酸钠加10mM醋酸铅为电解液溶液沉积结果,有灰黑色的明显沉积物,沉积不均匀。对比b和c可知,可以明显看到电解液为10mM醋酸铅沉积物颜色加深,说明其比5mM沉积量更多,这和i-t图所显示的结果相对应。

图3-13不同电解液沉积结果图,(a)1M醋酸钠电解液;(b)1M醋酸钠加5mM醋酸铅;(c)1M醋酸钠加10mM醋酸铅
在不同的沉积条件下同时进行了椭偏仪的监测。图3-14为不同条件下的椭偏结构模型,其中Au/Si基底上测得的数据,其物理模型如图3-14(a)所示;在池体中加入去离子水后的数据,其物理模型如图3-14(b)所示;1M醋酸钠溶液和5/10mM醋酸铅溶液的数据,其物理模型如图3-14(c)所示;1M醋酸钠溶液的数据,其物理模型如图3-14(d)所示。
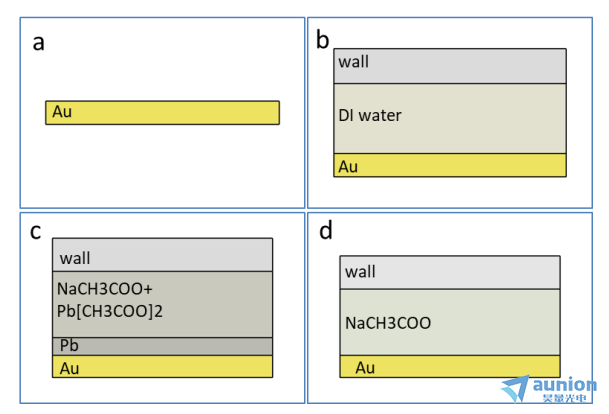
图3-14不同条件下的物理模型图:(a)Au/Si基底;(b)池体中加入去离子水;(c)池体中加入1M醋酸钠和10mM醋酸铅;(d)池体中加入1M醋酸钠
图3-15是不同条件下进行椭偏仪测量得到的椭偏参数Psi和Delta各自对比图。从图中可知,Psi和Delta的值大致的变化趋势一致,但是在位监测下有铅薄膜沉积的两组数据全程扰动较大,曲线上有许多的小峰,这是由于铅薄膜的沉积带来影响。

图3-15不同条件下(a)Psi和(b)Delta对比
实验说明该池体在位沉积铅薄膜椭偏仪测试得到的数据极具不稳定性,波动较大,且溶液浓度对椭偏数据的影响不明显,这和之前不同浓度测试的测试结果一致。
了解更多椭偏仪详情,请访问上海昊量光电的官方网页:
https://www.auniontech.com/three-level-56.html
更多详情请联系昊量光电/欢迎直接联系昊量光电
关于昊量光电:
上海昊量光电设备有限公司是光电产品专业代理商,产品包括各类激光器、光电调制器、光学测量设备、光学元件等,涉及应用涵盖了材料加工、光通讯、生物医疗、科学研究、国防、量子光学、生物显微、物联传感、激光制造等;可为客户提供完整的设备安装,培训,硬件开发,软件开发,系统集成等服务。
您可以通过我们昊量光电的官方网站www.auniontech.com了解更多的产品信息,或直接来电咨询4006-888-532。
相关文献:
[1] WONG H S P, FRANK D J, SOLOMON P M et al. Nanoscale cmos[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(4): 537-570.
[2] LOSURDO M, HINGERL K. ellipsometry at the nanoscale[M]. Springer Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London. 2013.
[3] DYRE J C. Universal low-temperature ac conductivity of macroscopically disordered nonmetals[J]. Physical Review B, 1993, 48(17): 12511-12526. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.48.12511.
[4] CHEN S, KÜHNE P, STANISHEV V et al. On the anomalous optical conductivity dISPersion of electrically conducting polymers: Ultra-wide spectral range ellipsometry combined with a Drude-Lorentz model[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(15): 4350-4362.
[5] 陈篮,周岩. 膜厚度测量的椭偏仪法原理分析[J]. 大学物理实验, 1999, 12(3): 10-13.
[6] ZAPIEN J A, COLLINS R W, MESSIER R. Multichannel ellipsometer for real time spectroscopy of thin film deposition from 1.5 to 6.5 eV[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(9): 3451-3460.
[7] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[8] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[9] YUAN M, YUAN L, HU Z et al. In Situ Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for Thermochromic CsPbI3 Phase Evolution Portfolio[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(14): 8008-8014.
[10] 焦杨景.椭偏仪在位表征电化学沉积的系统搭建.云南大学说是论文,2022.
[11] CANEPA M, MAIDECCHI G, TOCCAFONDI C et al. Spectroscopic ellipsometry of self assembLED monolayers: Interface effects. the case of phenyl selenide SAMs on gold[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(27): 11559-11565. DOI:10.1039/c3cp51304a.
[12] FUJIWARA H, KONDO M, MATSUDA A. Interface-layer formation in microcrystalline Si:H growth on ZnO substrates studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 93(5): 2400-2409.
[13] FUJIWARA H, TOYOSHIMA Y, KONDO M et al. Interface-layer formation mechanism in (formula presented) thin-film growth studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1999, 60(19): 13598-13604.
[14] LEE W K, KO J S. Kinetic model for the simulation of hen egg white lysozyme adsorption at solid/water interface[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 549-553.
[15] STAMATAKI K, PAPADAKIS V, EVEREST M A et al. Monitoring adsorption and sedimentation using evanescent-wave cavity ringdown ellipsometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(5): 1086-1093.
[16] VIEGAS D, FERNANDES E, QUEIRÓS R et al. Adapting Bobbert-Vlieger model to spectroscopic ellipsometry of gold nanoparticles with bio-organic shells[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(8): 3538.
[17] ARWIN H. Application of ellipsometry techniques to biological materials[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(9): 2589-2592.
[18] ZIMMER A, VEYS-RENAUX D, BROCH L et al. In situ spectroelectrochemical ellipsometry using super continuum white laser: Study of the anodization of magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2019, 37(6): 062911.
[19] ZANGOOIE S, BJORKLUND R, ARWIN H. Water Interaction with Thermally Oxidized Porous Silicon Layers[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(11): 4027-4035.
[20] KYUNG Y B, LEE S, OH H et al. Determination of the optical functions of various liquids by rotating compensator multichannel spectroscopic ellipsometry[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2005, 26(6): 947-951.
[21] OGIEGLO W, VAN DER WERF H, TEMPELMAN K et al. Erratum to ― n-Hexane induced swelling of thin PDMS films under non-equilibrium nanofiltration permeation conditions, resolved by spectroscopic ellipsometry‖ [J. Membr. Sci. 431 (2013), 233-243][J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 437: 312..
[22] BROCH L, JOHANN L, STEIN N et al. Real time in situ ellipsometric and gravimetric monitoring for electrochemistry experiments[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2007, 78(6).
[23] BISIO F, PRATO M, BARBORINI E et al. Interaction of alkanethiols with nanoporous cluster-assembled Au films[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(13): 8371-8376.
[24] 李广立. 氧化亚铜薄膜的制备及其光电性能研究[D]. 西南交通大学, 2016.
[25] 董金矿. 氧化亚铜薄膜的制备及其光催化性能的研究[D]. 安徽建筑大学, 2014.
[26] 张桢. 氧化亚铜薄膜的电化学制备及其光催化和光电性能的研究[D]. 上海交通大学材料科 学与工程学院, 2013.
[27] DISSERTATION M. Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film[J]. 2017.
[28] NIE J, YU X, HU D et al. Preparation and Properties of Cu2O/TiO2 heterojunction Nanocomposite for Rhodamine B Degradation under visible light[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(27): 8118-8128.
[29] STRASSER P, GLIECH M, KUEHL S et al. Electrochemical processes on solid shaped nanoparticles with defined facets[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(3): 715-735.
[30] XU Z, CHEN Y, ZHANG Z et al. Progress of research on underpotential deposition——I. Theory of underpotential deposition[J]. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/ Acta Physico - Chimica Sinica, 2015, 31(7): 1219-1230.
[31] PANGAROV n. Thermodynamics of electrochemical phase formation and underpotential metal deposition[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(6): 763-775.
[32] KAYASTH S. ELECTRODEPOSITION STUDIES OF RARE EARTHS[J]. Methods in Geochemistry and Geophysics, 1972, 6(C): 5-13.
[33] KONDO T, TAKAKUSAGI S, UOSAKI K. Stability of underpotentially deposited Ag layers on a Au(1 1 1) surface studied by surface X-ray scattering[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(4): 804-807.
[34] GASPAROTTO L H S, BORISENKO N, BOCCHI N et al. In situ STM investigation of the lithium underpotential deposition on Au(111) in the air- and water-stable ionic liquid 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(47): 11140-11145.
[35] SARABIA F J, CLIMENT V, FELIU J M. Underpotential deposition of Nickel on platinum single crystal electrodes[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 819(V): 391-400.
[36] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R, SWAIN E et al. Fundamentals and Applications[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2001.
[37] SCHWEINER F, MAIN J, FELDMAIER M et al. Impact of the valence band structure of Cu2O on excitonic spectra[J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 93(19): 1-16.
[38] XIONG L, HUANG S, YANG X et al. P-Type and n-type Cu2O semiconductor thin films: Controllable preparation by simple solvothermal method and photoelectrochemical properties[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(6): 2735-2739.
[39] KAZIMIERCZUK T, FRÖHLICH D, SCHEEL S et al. Giant Rydberg excitons in the copper oxide Cu2O[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7522): 343-347.
[40] RAEBIGER H, LANY S, ZUNGER A. Origins of the p-type nature and cation deficiency in Cu2 O and related materials[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2007, 76(4): 1-5.
[41] 舒云. Cu2O薄膜的电化学制备及其光电化学性能的研究[D]. 云南大学物理与天文学院,2019.
展示全部 